How to input imperfections in Member
All kinds of imperfections are described in the Theoretical background for IDEA StatiCa Member. In short, the global imperfection is applied to the whole structural model, and local imperfection is applied to single beams, columns, or frames.
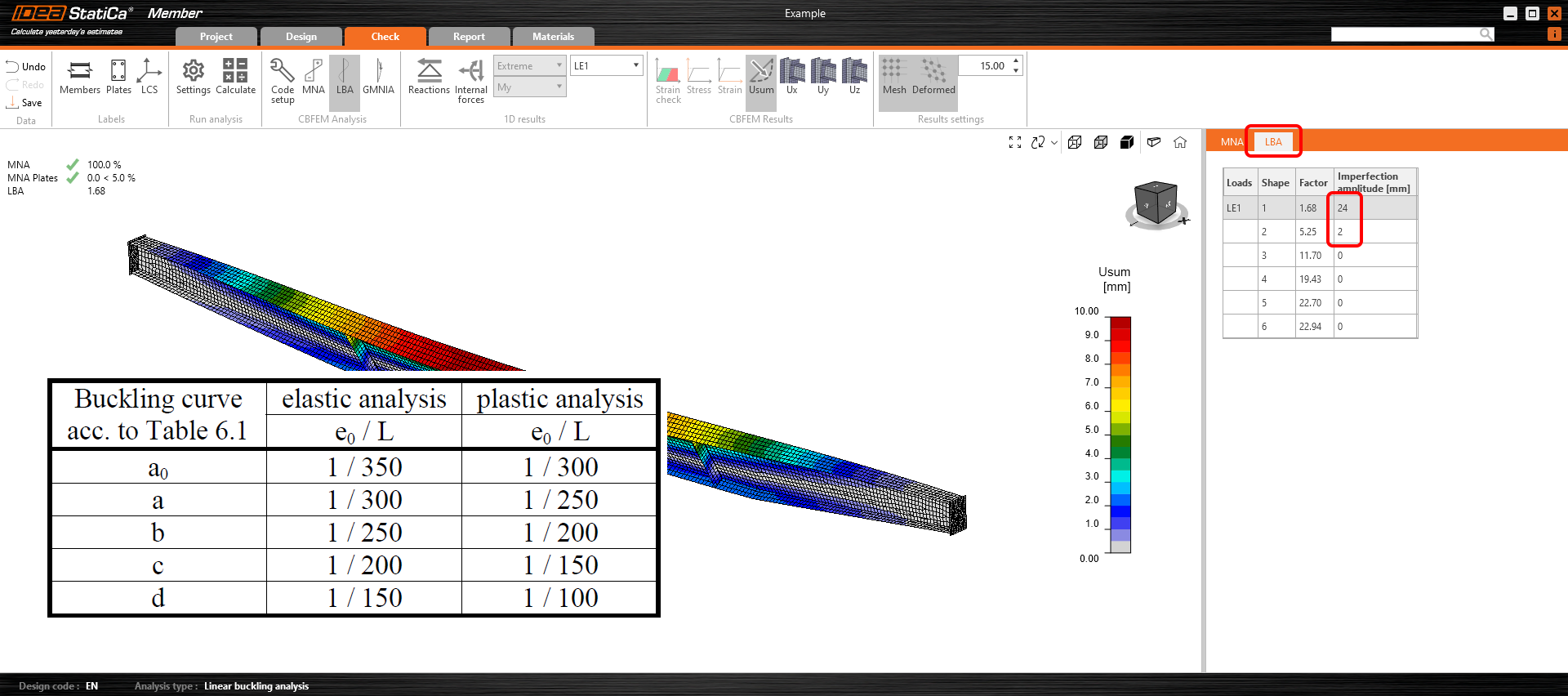
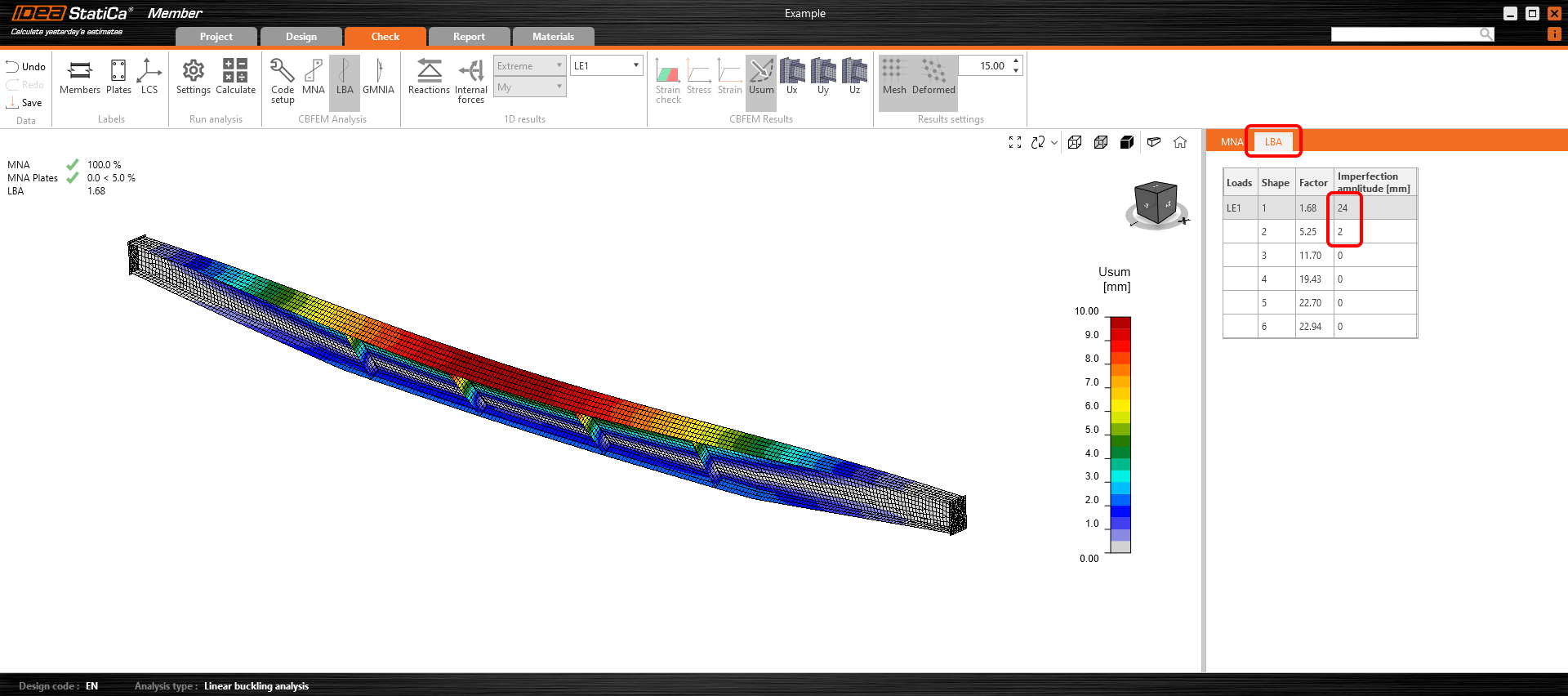
IDEA StatiCa Member allows the application of the local imperfections to the buckling shapes with amplitudes e0 in millimeters determined by the user. The e0 value is calculated as a relative value related to the member length. If both directions are possible for deflection, it is crucial to analyze both buckling shapes - with positive + and negative - signs of e0.
Usually, the first buckling shape with the maximum amplitude according to relevant guidelines is enough. More buckling mode shapes should be analyzed for models with multiple analyzed members.
There are guidelines for each code on how to determine imperfections, which you input in Member for the GMNIA analysis.
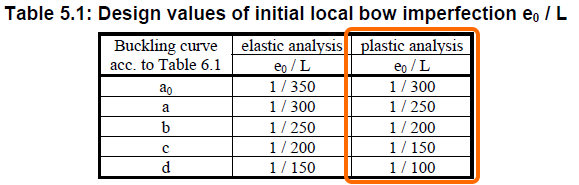
For instance, in Eurocode, it is described in EN 1993-1-1, Cl.5.3.2 (3). The imperfection amplitude e0 is calculated in Table 5.1, where the plastic analysis should be used.
To determine the buckling curve in the tab, you need to decide, based on the displayed buckling shape in LBA analysis in Member, whether:
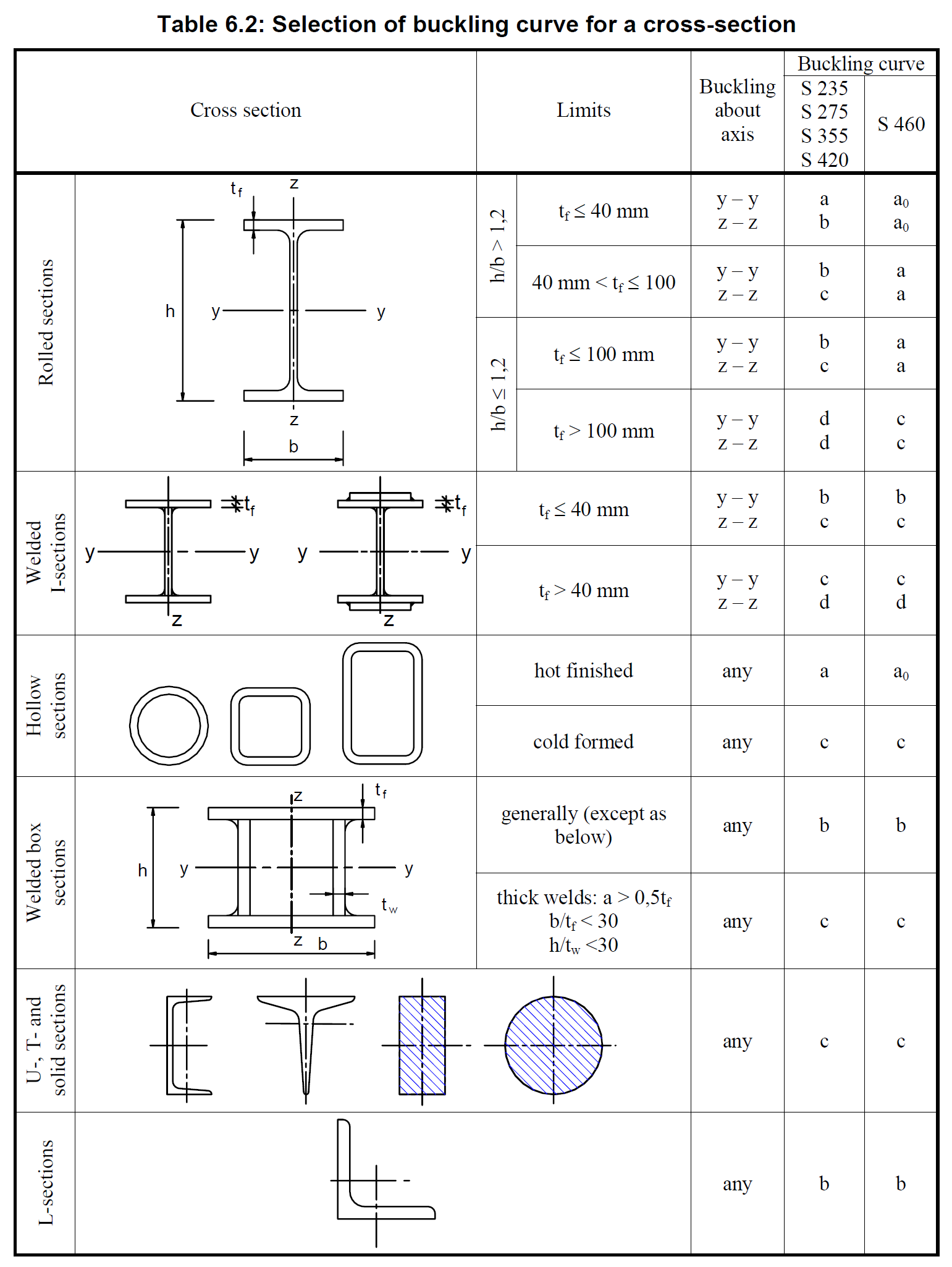
- Member is predominantly compressed where flexural, torsional, or torsional-flexural buckling is expected, and use Table 6.2,
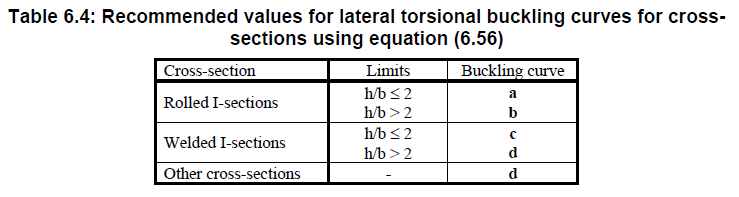
- Or if the member is predominantly bent and the main failure mode is lateral-torsional buckling, and use Table 6.4.
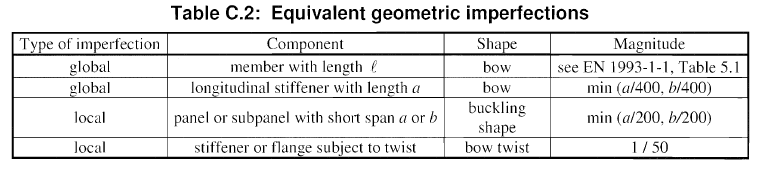
For buckling of panels (beam web), flanges, and stiffeners, table C.2 from EN 1993-1-5 should be used to calculate the imperfection values.
The determined imperfection amplitudes can be input in the tab after the LBA (linear buckling analysis) and before the 2nd order GMNIA analysis (geometrically and materially nonlinear analysis with imperfections).
Positive + and negative - values of imperfections e0 should be applied consecutively, and the more dangerous results should be considered relevant. If imperfections are applied to more buckling shapes, all possible combinations of + and - imperfection values should be calculated.