Implementation of long-term losses in Detail
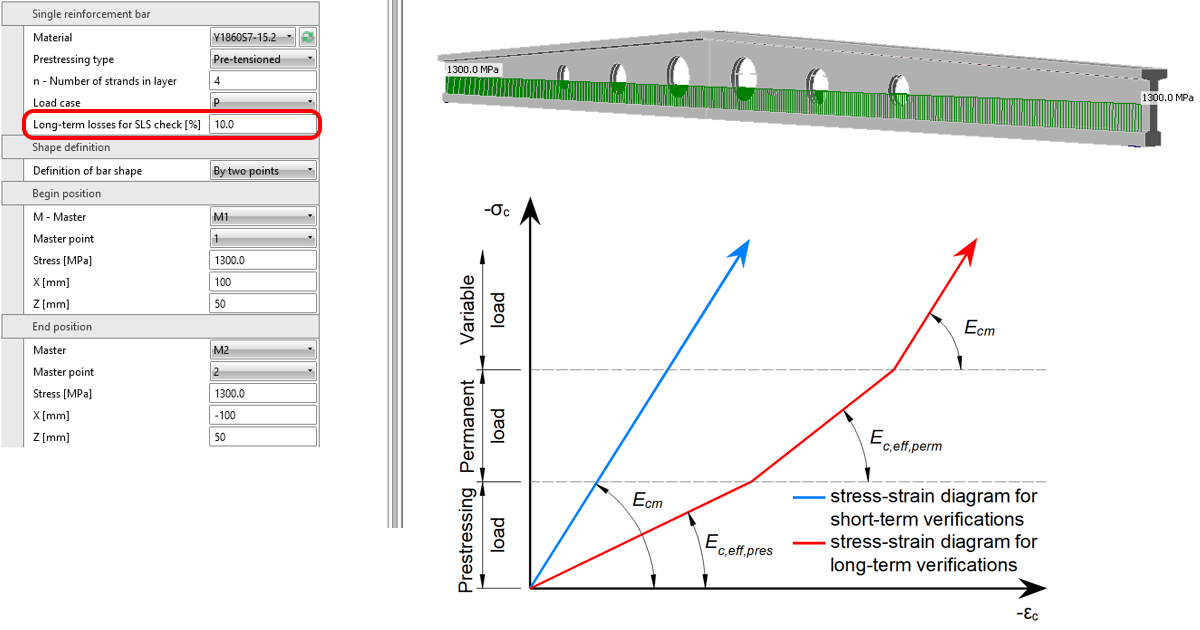
From version 23.0, you can set the estimation for long-term losses for pre-tensioned and post-tensioned tendons. It means that you won't have to complicatedly create special combinations with different prestressing coefficients to assess the structure at the beginning and end of its service life. A new entity in the properties of prestressing tendon called Long-term losses for SLS check [%] is now available, which allows you to check the short-term and long-term effects within one combination.
After calculation, you can switch between long-term and short-term to see the different results affected by the different material models as well as different initial stresses in the tendon.
How does it work? Read the following text to explore all the consequences of this new functionality.
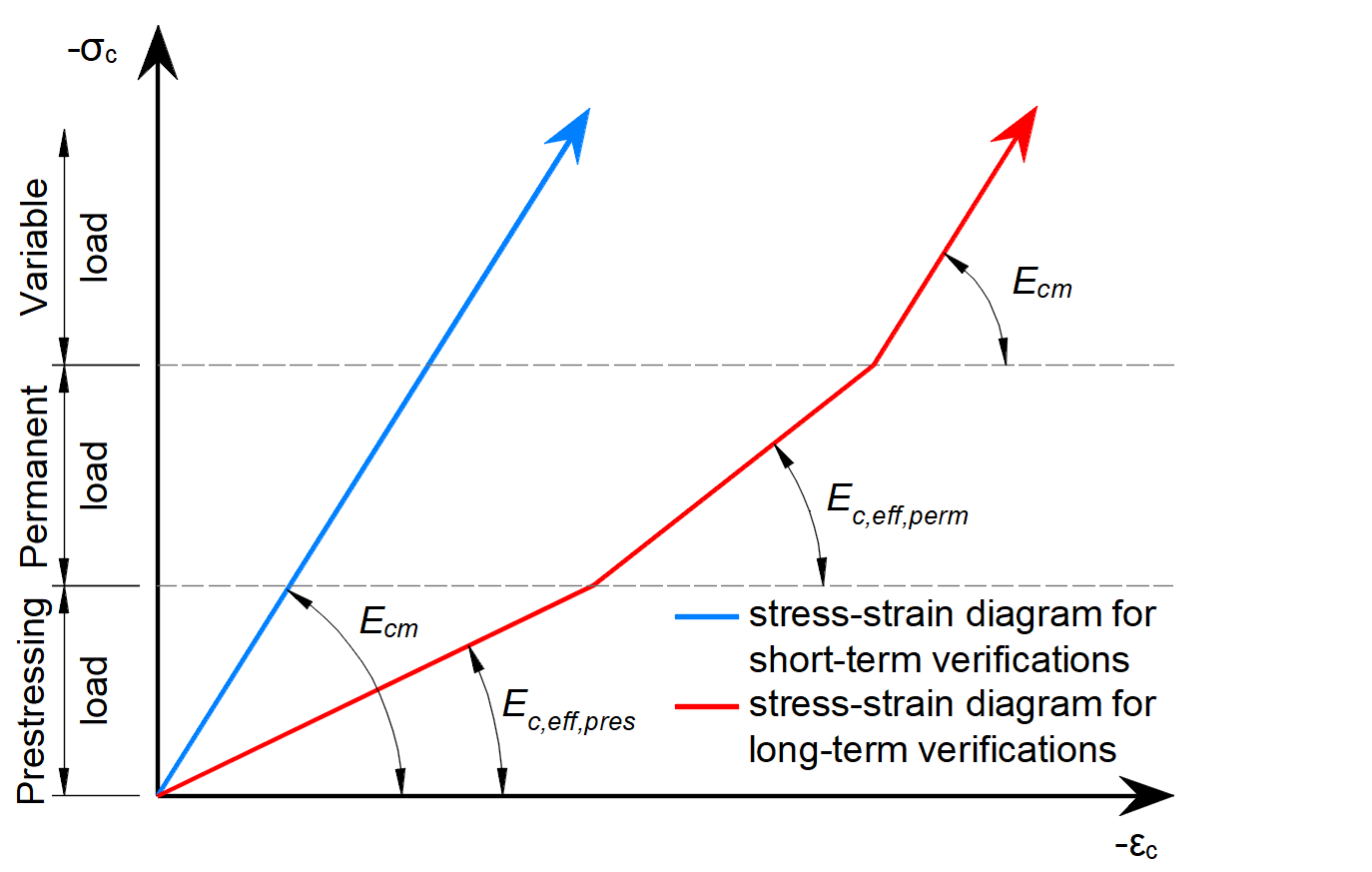
For the calculation of the long-term effect in SLS checks, the values of stresses in the prestressing reinforcement are reduced by the defined value of the long-term losses. In other words, reduced stress by the estimation of long-term losses is used for prestressing increment where the Ec,eff,press is used.
The value of long-term losses for SLS check [%], which should be set for pre-tensioned and post-tensioned tendons, differs. Here's why.
Pre-tensioned tendons
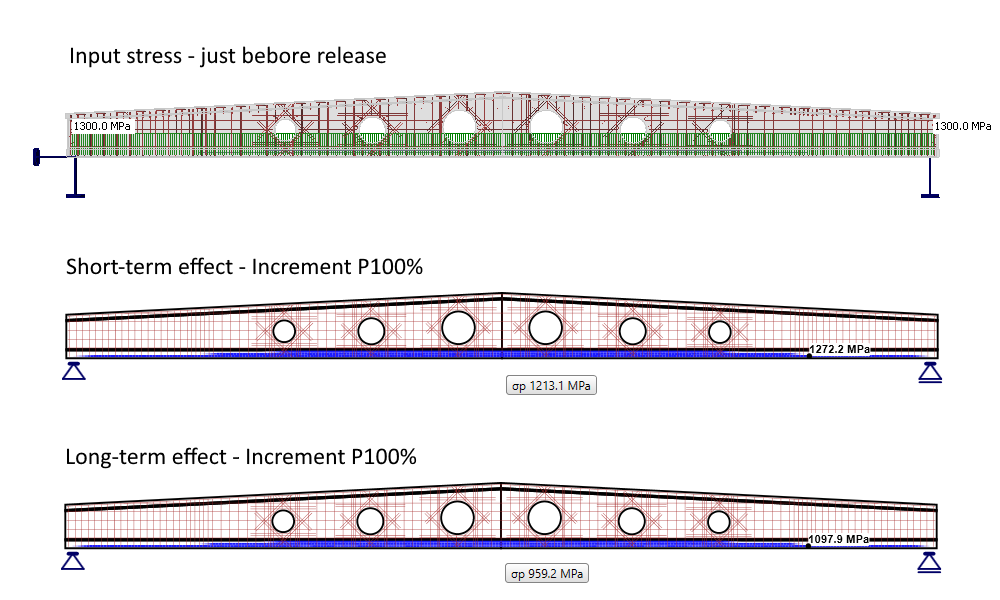
For pre-tensioned tendons, the input stress is the stress just before the release from abutments (stress after short-term losses due to anchorage set -> slip, deformation of abutments, short-term relaxation, etc.). The elastic strain in concrete is automatically calculated with the corresponding material model (Ecm is used for short-term effects, and Ec,eff,press is used for long-term effects). It follows that the long-term losses for the SLS check [%] is the value defining long-term losses caused by shrinkage and long-term relaxation. The default value is 10%.
As you can see in the figure below, there are now three types of stress.
- Input stress just before the release
- Stress after short-term losses
- Stress after long-term losses
Note that the self-weight is defined as a prestressing load type. The first increment (including self-weight) prestressing is shown.
Post-tensioned tendons
For post-tensioned tendons, the input stress is the stress after short-term losses, or you can set the anchorage stress and get the program to calculate the short-term losses automatically. Short-term losses, in this case, are – friction, immediate elastic strain in concrete, and anchorage set -> slip. It follows that the long-term losses for SLS check [%] is the value defining long-term losses caused by creep, shrinkage, and long-term relaxation. The default value is 10%.
As you can see in the figure below, there are now two types of stress.
- Input stress = Stress after short-term losses
- Stress after long-term losses
Note that the self-weight is defined as a prestressing load type. The first increment (including self-weight) prestressing is shown.
Available in Enhanced editions of IDEA StatiCa Prestressing.