Stiffness analysis
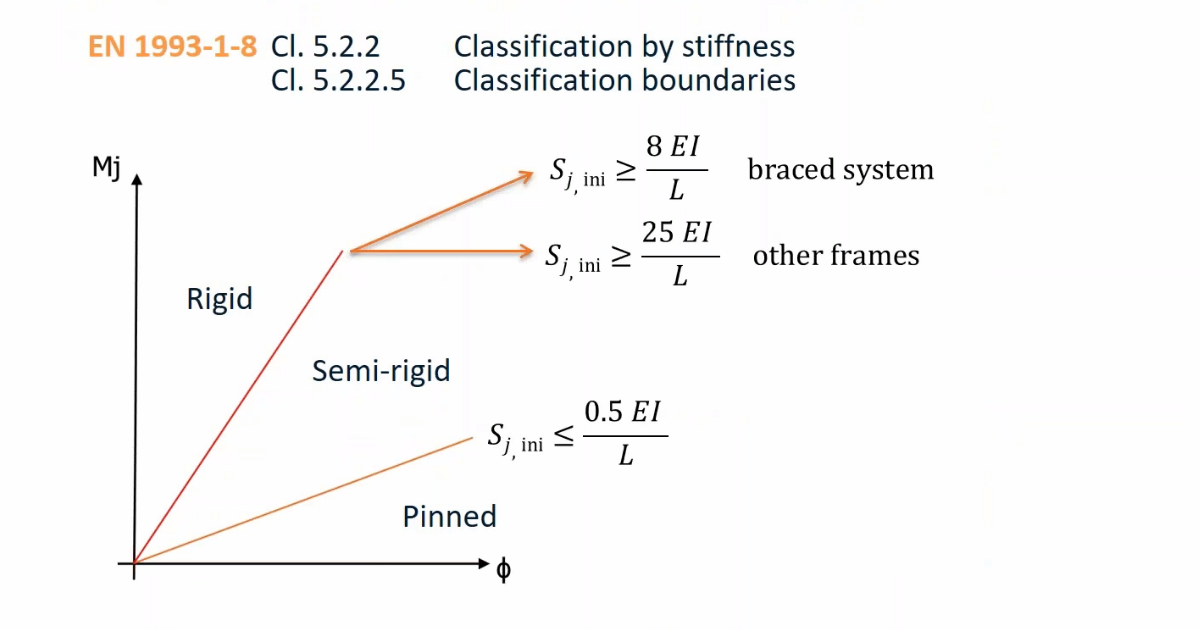
Use stiffness analysis in IDEA StatiCa Connection to determine whether the joints are pinned, semirigid, or rigid. The classification of the connection follows the selected national standard.
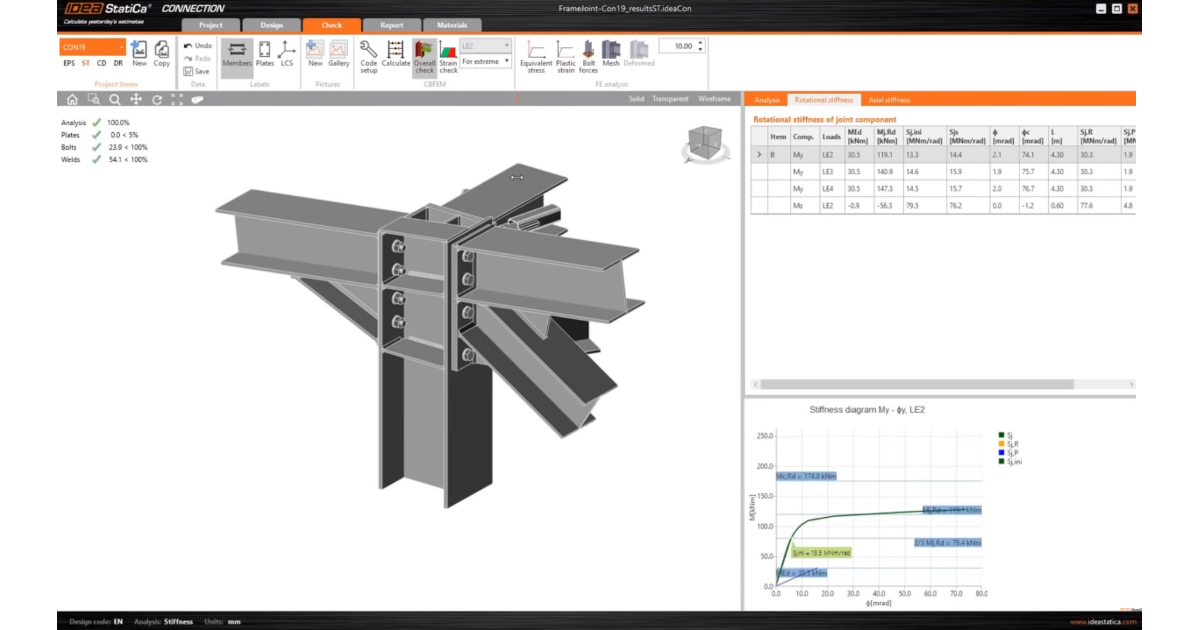
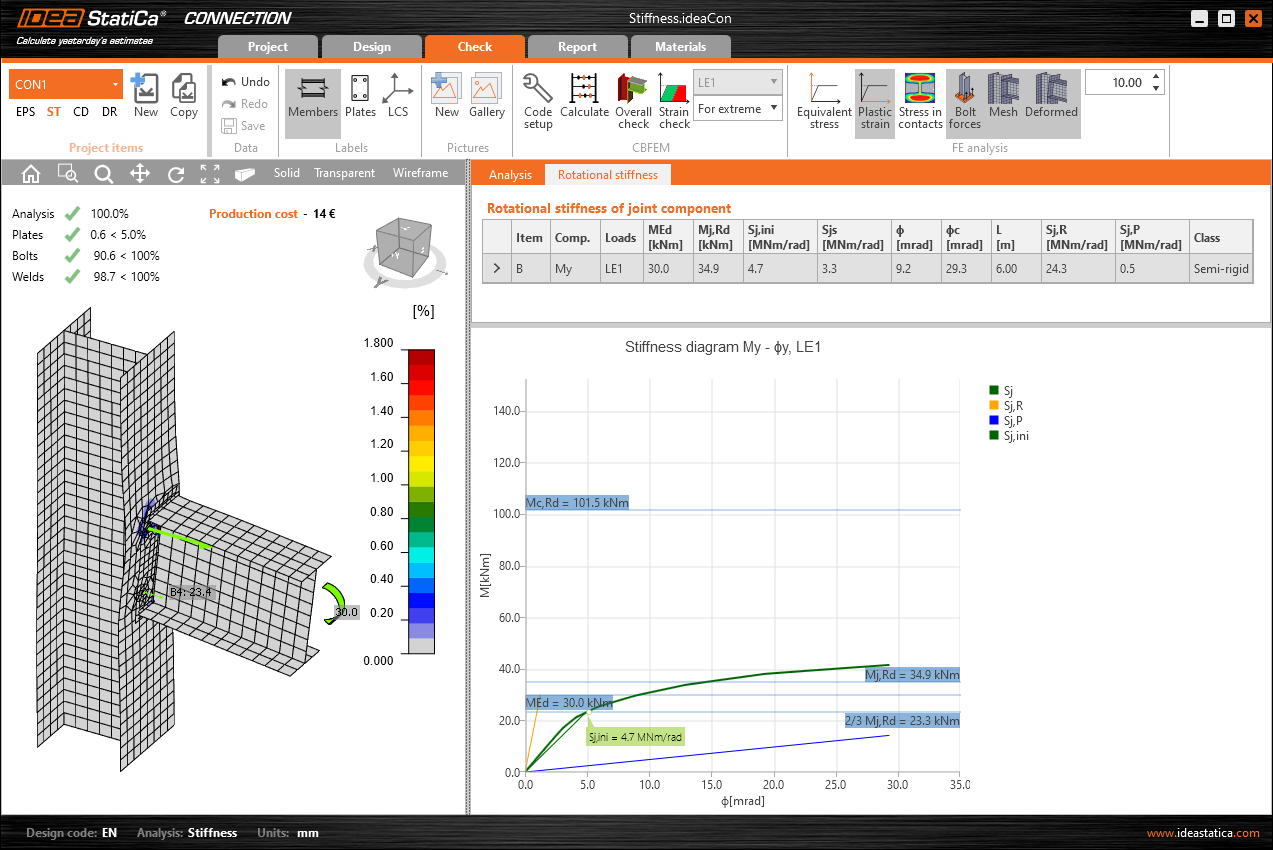
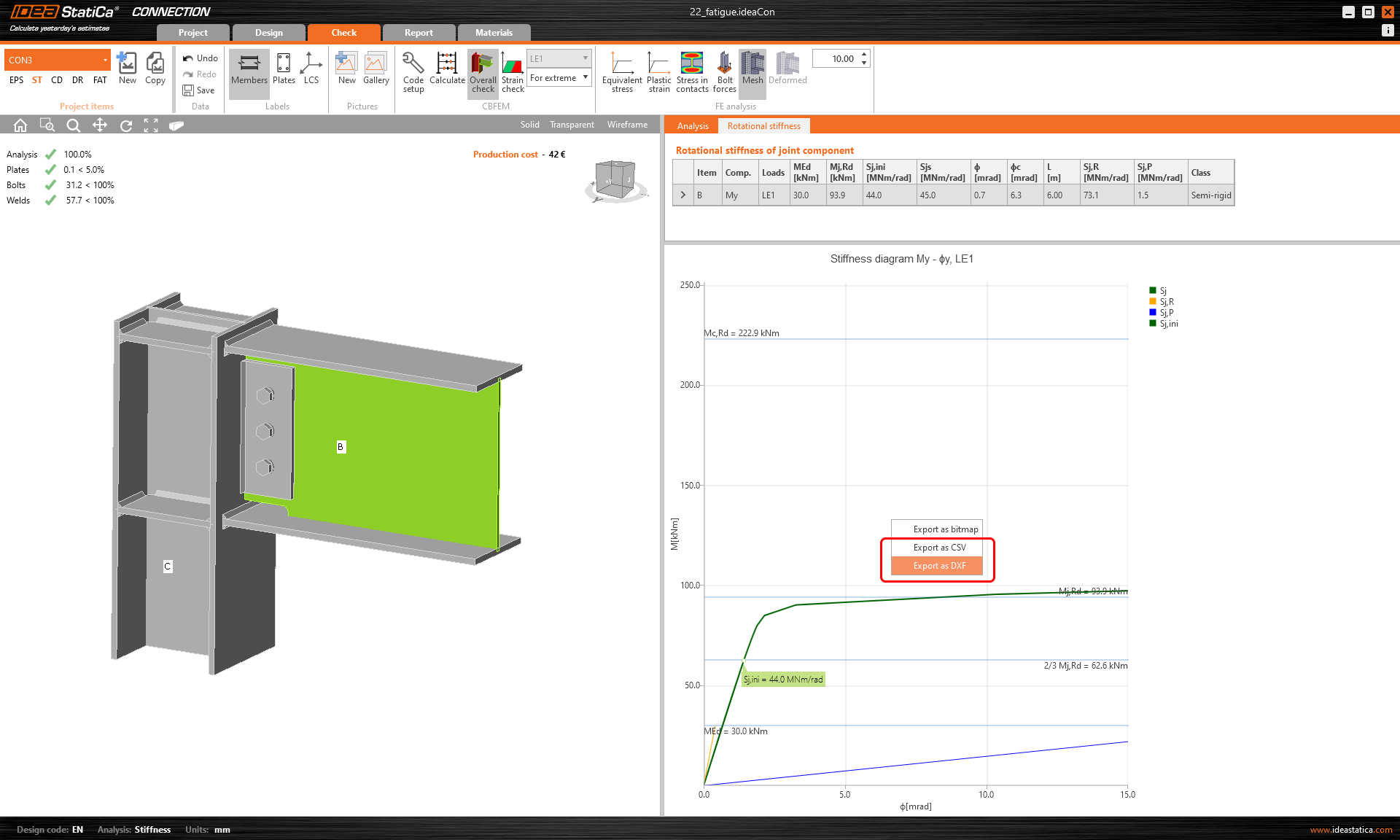
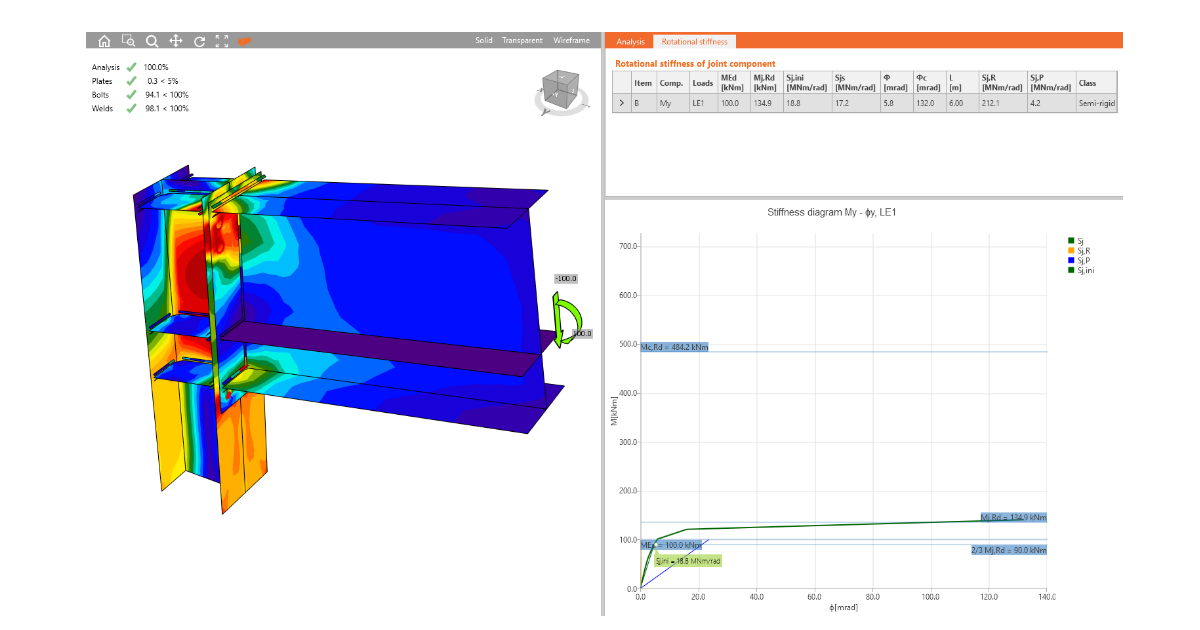
As a result of the stiffness analysis, you will get the moment-rotation diagram and a table with several values. Based on the curve and a selected standard, the joint is assigned with the
- pinned
- rigid
- semirigid class.
Further parameters have to be set to analyze the stiffness properly
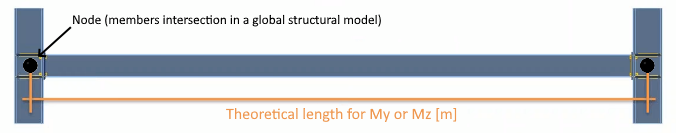
- theoretical length of the member
- proper load - N, My, Mz, or combinations
- braced system parameter
The Theoretical length for My and Mz [m] is defined as the node-to-node distance of the analyzed member and is used for classification only (not for calculating the actual stiffness values).
The braced system (braced frame) option is available for projects in Eurocode as per EN 1993-1-8.
There are several sources of information to read about this type of analysis. We recommend reading the general part of the Theoretical Background, the blogpost Why bother with connection stiffness and/or watching one of our webinars on the topic (see below).
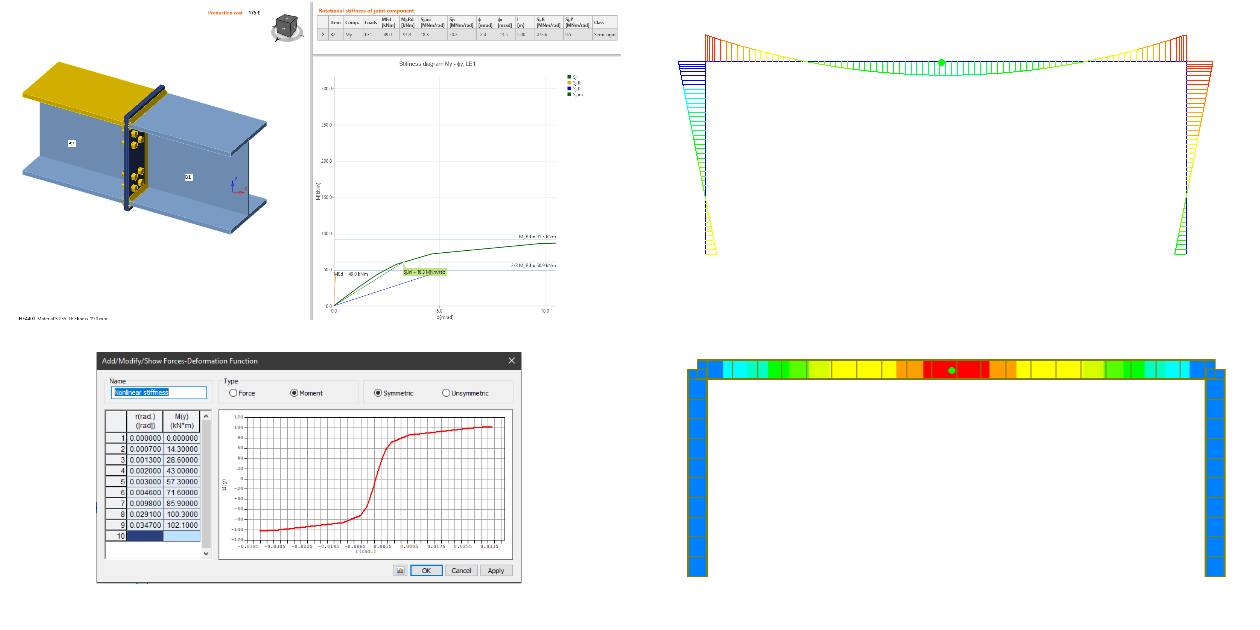
To combine the stiffness results with your global FEA model, go through Connection stiffness and its use in global analysis article and/or watch How to put rotational stiffness into your FEA model video.
At the end of the article, you can find several step-by-step tutorials.
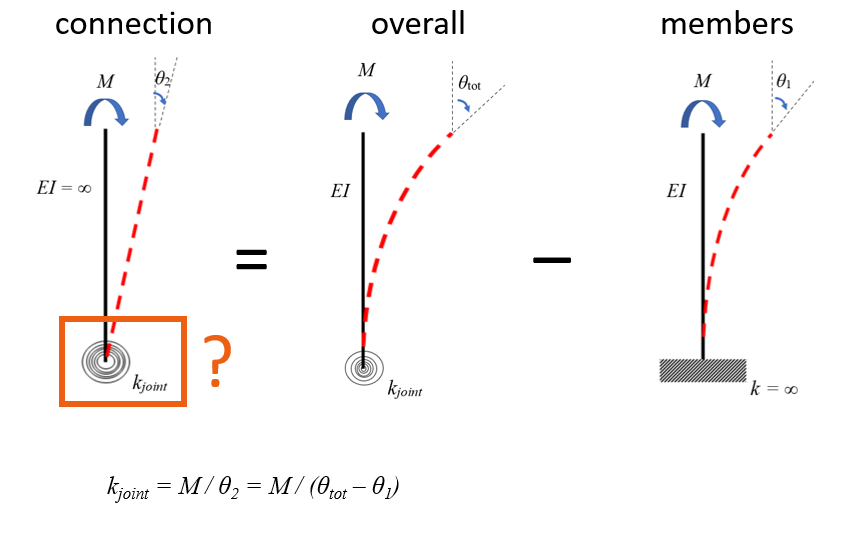
Model for stiffness evaluation
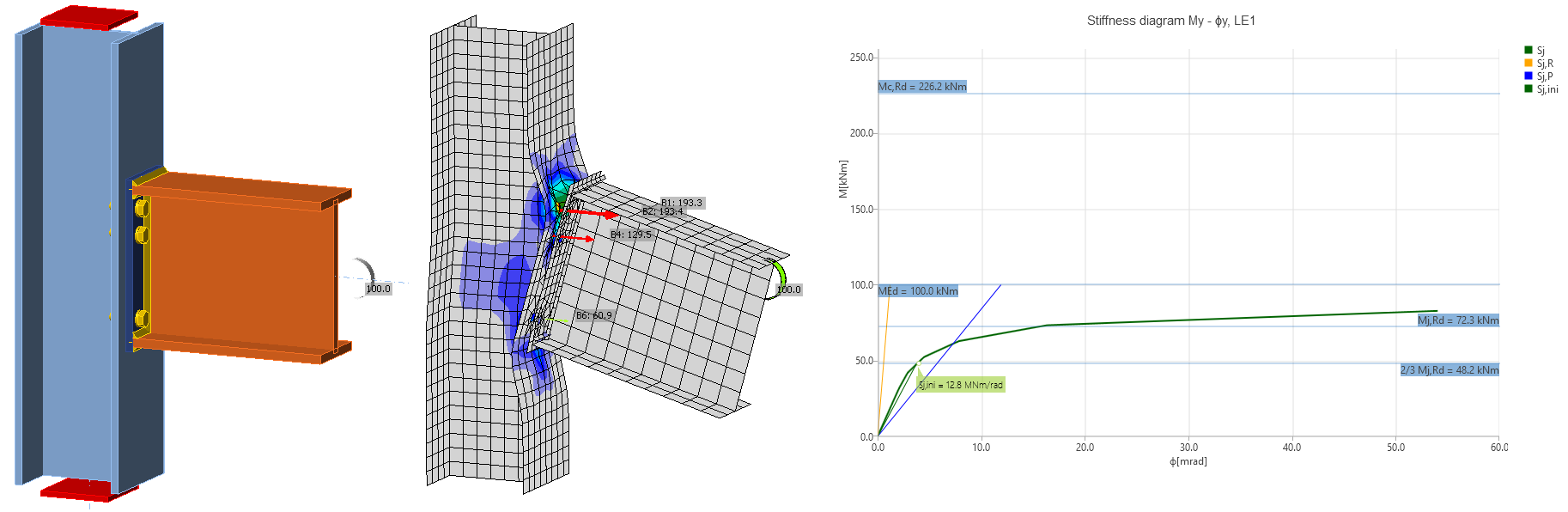
To evaluate the rotational stiffness kjoint of the connection itself and the corresponding rotation θ2, we subtract the part of the stiffness assigned to the deformation of members θ1 from the overall deformation θtot.
The rotation of members θ1 is evaluated on the model with ideally rigid connections among all members. The overall rotation θtot is evaluated on the model with real manufacturing operations.
The results obtained from the stiffness analysis correspond to the kjoint and θ2.
Infinite or very high value of Sj,ini
If the Sj,ini and Sj,s show infinite stiffness, this means the stiffness curve is so steep that its actually 90° in the diagram so that the tangent results in infinity. This always means a rigid connection far from the border of semi-rigid class, so the exact values are not important. In other words, the connection is absolutely stiff.
Theoretical Background
Read the essential information about stiffness analysis in our Theoretical Background. The above-mentioned settings are described in the general part of it.
The general part of the Theoretical Background about the stiffness analysis and its results:
Stiffness analysis and deformation capacity of steel joints
Specific parts of the Theoretical Background for each of the supported national standards:
- Joint classification according to Eurocode (EN)
- Steel joint classification according to American Standard (AISC)
- Steel joint classification according to Canadian standard (CISC)
- Joint classification according to Australian standards (AS)
- Classification according to stiffness for Indian standard (IS)
- Classification according to stiffness for Hong Kong Code (HKG)
- Joint classification according to Chinese standard (GB)
- Joint classification according to Russian standards (SP)
Other articles on connection stiffness and verifications
You can find more detailed information and some verification studies in the following articles. Some of them are part of the book "Benchmark Cases for Advanced Design of Structural Steel Connections" written by prof. Wald and his team.
- Connection stiffness and its use in global analysis
- Stiffness analysis - W to HSS moment connection (AISC)
- Bending stiffness of bolted joint of open sections
- Bending stiffness of welded joint of open sections
- Why bother with connection stiffness (blogpost)
Webinars and videos
In the past, we have held several webinars on the topic of the stiffness of the connection. Also, some other videos describe how to work in the application. You can find inspiration from real-life projects as well as hints for setting up your computational models correctly.
Connection Wednesdays - Stiffness classification
In this webinar, we briefly review the code requirements related to stiffness classification. Afterward, we endeavor to design the connections of an actual frame that will be initially designed as moment resisting. We employ a semi-rigid configuration and subsequently apply the predicted behavior to the global analysis structure. Throughout this process, we explore common questions and assess their impact on the design.
Connection Wednesdays - Game-changing joint stiffness analysis
During the webinar, you will see the whole workflow of modeling, loading, and code-check of one interesting steel joint.
Connection Wednesdays - Residence in Ružomberok joint
Platform joints should be usually pinned, but what if the reality is not so simple? How to input the joint stiffness analysis correctly? See the frame joint stiffness analysis and consequences of the stiffness to FEM model.
How to put rotational stiffness into your FEA model
The stiffness of the joint is a significant and indispensable factor in the design of the global structure for semirigid connections. The question is, where can I calculate the stiffness of the joint, and what stiffness should be used for my design?
Design and code check of joint from Jakarta velodrome
The following webinar recording explains how the stiffness analysis diagram is constructed, what the settings are, and what results you will get.
Updates in versions
The following features are part of our release notes of IDEA StatiCa and may be related to the stiffness analysis. Read more about the features in the dedicated articles under the link.
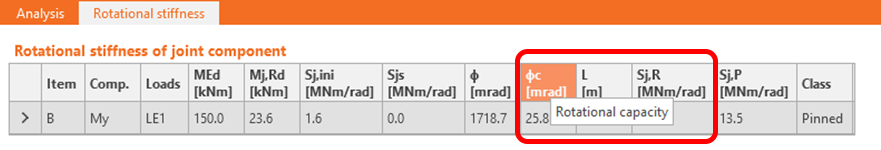
Rotational capacity limited by bolt and weld failure (Stiffness analysis) (version 21.0)
Export of moment-rotation curve to CSV and DXF (version 22.0)
Tutorials
We have created step-by-step tutorials to set up the model and run the analysis. Find the links to them below:
Stiffness analysis of a steel connection (EN)
Stiffness analysis of a steel connection (AISC)
Rotational stiffness of a haunched beam